NMN
What is NMN?
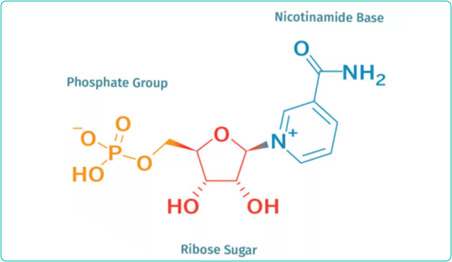
NMN stands for nicotinamide mononucleotide, a molecule that naturally exists in all life forms. At the molecular level, this molecule is ribonucleotide, which is the basic structural unit of nucleic acid RNA. In structure, it is composed of nicotinamide group, ribose and phosphate group (Fig. 1). NMN is the direct precursor of the essential molecule nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+), and is considered to be the key molecule to increase the level of NAD+in cells.
NMN stands for nicotinamide mononucleotide, a molecule that naturally exists in all life forms. At the molecular level, this molecule is ribonucleotide, which is the basic structural unit of nucleic acid RNA. In structure, it is composed of nicotinamide group, ribose and phosphate group (Fig. 1). NMN is the direct precursor of the essential molecule nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+), and is considered to be the key molecule to increase the level of NAD+in cells.
What is NAD+?
NAD+is an essential coenzyme for life and cell function. Enzymes are catalysts that make biochemical reactions possible. Coenzymes are "auxiliary" molecules required for enzymes to function. NAD+is the most abundant molecule in the human body except water. Without water, organisms will die. NAD+is used by many proteins in the body (such as silencing regulatory proteins), which can repair damaged DNA. It is also important for mitochondria, which are the power source of cells and produce chemical energy used by human body.
NAD+is an essential coenzyme for life and cell function. Enzymes are catalysts that make biochemical reactions possible. Coenzymes are "auxiliary" molecules required for enzymes to function. NAD+is the most abundant molecule in the human body except water. Without water, organisms will die. NAD+is used by many proteins in the body (such as silencing regulatory proteins), which can repair damaged DNA. It is also important for mitochondria, which are the power source of cells and produce chemical energy used by human body.
NAD+acts as a coenzyme in mitochondria
NAD+plays a particularly active role in metabolic processes (such as glycolysis, TCA cycle (also known as Krebs cycle or citric acid cycle) and electron transport chain. This movement occurs in our mitochondria, which is also our way to obtain cell energy.
NAD+acts as a ligand, binds with enzymes and transfers electrons between molecules. Electrons are the atomic basis of cell energy. By transferring them from one molecule to another, NAD+acts through a cellular mechanism similar to battery charging. When electrons are consumed to provide energy, the battery will run out. These electrons cannot return to their starting point without a booster. In cells, NAD+can play a promoting role. In this way, NAD+can reduce or increase enzyme activity, gene expression and cell signal transduction.
NAD+plays a particularly active role in metabolic processes (such as glycolysis, TCA cycle (also known as Krebs cycle or citric acid cycle) and electron transport chain. This movement occurs in our mitochondria, which is also our way to obtain cell energy.
NAD+acts as a ligand, binds with enzymes and transfers electrons between molecules. Electrons are the atomic basis of cell energy. By transferring them from one molecule to another, NAD+acts through a cellular mechanism similar to battery charging. When electrons are consumed to provide energy, the battery will run out. These electrons cannot return to their starting point without a booster. In cells, NAD+can play a promoting role. In this way, NAD+can reduce or increase enzyme activity, gene expression and cell signal transduction.
NAD+helps control DNA damage
As organisms age, they will suffer DNA damage due to environmental factors such as radiation, pollution and inaccurate DNA replication. According to the current aging theory, the accumulation of DNA damage is the main cause of aging. Almost all cells contain "molecular machinery" to repair such damage. This machine consumes NAD+and energy molecules. Therefore, excessive DNA damage will consume valuable cell resources.
An important DNA repair protein PARP (poly (ADP ribose) polymerase) relies on NAD+to function. The level of NAD+in the elderly decreased. The accumulation of DNA damage caused by normal aging process leads to the increase of PARP, which leads to the decrease of NAD+concentration. Any further DNA damage in mitochondria will aggravate this consumption.
As organisms age, they will suffer DNA damage due to environmental factors such as radiation, pollution and inaccurate DNA replication. According to the current aging theory, the accumulation of DNA damage is the main cause of aging. Almost all cells contain "molecular machinery" to repair such damage. This machine consumes NAD+and energy molecules. Therefore, excessive DNA damage will consume valuable cell resources.
An important DNA repair protein PARP (poly (ADP ribose) polymerase) relies on NAD+to function. The level of NAD+in the elderly decreased. The accumulation of DNA damage caused by normal aging process leads to the increase of PARP, which leads to the decrease of NAD+concentration. Any further DNA damage in mitochondria will aggravate this consumption.
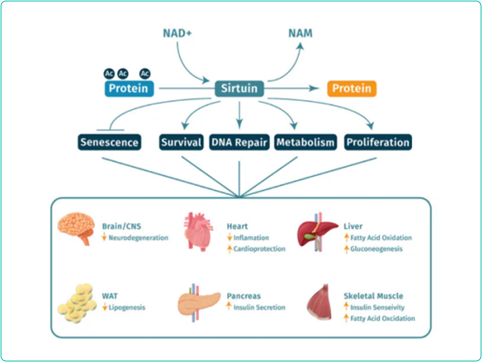
How NAD+affects sirtuins (longevity gene) activity
The newly discovered sirtuins, also known as "guardians of genes", play a vital role in maintaining cell health. Sirtuins is a family of enzymes involved in cell stress response and damage repair. They are also involved in insulin secretion, the aging process and aging related health conditions, such as neurodegenerative diseases and diabetes. NAD+is required for activation of silencing regulatory proteins.
As David Sinclair, a geneticist and NAD researcher at Harvard University, said, as we grow older, we will lose NAD+. "Therefore, the decline in the activity of Thursine is considered to be the main reason for our body to develop diseases in old age, but not in young age." He believed that the level of NAD+will naturally increase during aging, which may slow down or reverse some aging processes.
The newly discovered sirtuins, also known as "guardians of genes", play a vital role in maintaining cell health. Sirtuins is a family of enzymes involved in cell stress response and damage repair. They are also involved in insulin secretion, the aging process and aging related health conditions, such as neurodegenerative diseases and diabetes. NAD+is required for activation of silencing regulatory proteins.
As David Sinclair, a geneticist and NAD researcher at Harvard University, said, as we grow older, we will lose NAD+. "Therefore, the decline in the activity of Thursine is considered to be the main reason for our body to develop diseases in old age, but not in young age." He believed that the level of NAD+will naturally increase during aging, which may slow down or reverse some aging processes.
Why should we care about NAD+?
Since the discovery of NAD+in 1906, scientists have paid attention to this molecule because of its abundance in the body and its key role in maintaining the molecular pathway of human body operation. In animal research, improving the level of NAD+in the body has shown encouraging results in the fields of metabolism and age-related diseases, and even some anti-aging properties. Age related diseases, such as diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, neurodegenerative diseases and immune system decline generally.
Since the discovery of NAD+in 1906, scientists have paid attention to this molecule because of its abundance in the body and its key role in maintaining the molecular pathway of human body operation. In animal research, improving the level of NAD+in the body has shown encouraging results in the fields of metabolism and age-related diseases, and even some anti-aging properties. Age related diseases, such as diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, neurodegenerative diseases and immune system decline generally.
NMN as NAD+supplement
With the passage of time, the intracellular concentration of NAD+will decrease with aging after the normal cell function depletes the supply of NAD+. The health level of NAD+is believed to be restored by supplementation of NAD+precursors. According to the study, precursors such as NMN and nicotinamide nucleoside (NR) are considered as supplements to the production of NAD+, which increases the concentration of NAD+. David Sinclair, a researcher of NAD+at Harvard University, said: "It is an unrealistic choice to feed or apply NAD+directly to organisms. NAD+molecules cannot easily pass through the cell membrane and enter into cells, so they will not actively affect metabolism. On the contrary, the precursors of NAD+must be used to improve the bioavailability of NAD+." This means that NAD+cannot be directly absorbed because it is not easy to absorb. NAD+precursor is more easily absorbed than NAD+and is a more effective supplement.
With the passage of time, the intracellular concentration of NAD+will decrease with aging after the normal cell function depletes the supply of NAD+. The health level of NAD+is believed to be restored by supplementation of NAD+precursors. According to the study, precursors such as NMN and nicotinamide nucleoside (NR) are considered as supplements to the production of NAD+, which increases the concentration of NAD+. David Sinclair, a researcher of NAD+at Harvard University, said: "It is an unrealistic choice to feed or apply NAD+directly to organisms. NAD+molecules cannot easily pass through the cell membrane and enter into cells, so they will not actively affect metabolism. On the contrary, the precursors of NAD+must be used to improve the bioavailability of NAD+." This means that NAD+cannot be directly absorbed because it is not easy to absorb. NAD+precursor is more easily absorbed than NAD+and is a more effective supplement.
How can NMN supplements be absorbed and distributed in the body?
NMN seems to be absorbed into cells through molecular transporters embedded in the cell surface. NMN molecules are smaller than NAD+and can be more effectively absorbed into cells. Because the cell membrane presents a barrier, NAD+cannot easily enter the human body. The membrane has water-free space, which can prevent ions, polar molecules and macromolecules from entering without using transport proteins. It was thought that NMN must be changed before entering the cell, but new evidence shows that it can enter the cell membrane directly through NMN-specific transport protein.
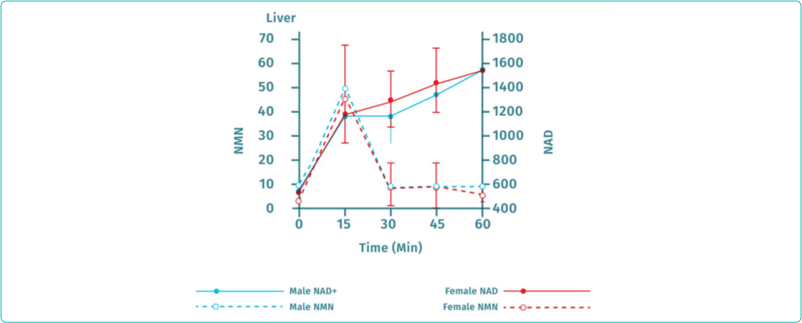
In addition, the injection of NMN will lead to the increase of NAD+in many areas of the body (including pancreas, adipose tissue, heart, skeletal muscle, kidney, testis, eyes and blood vessels). Oral administration of NMN in mice will increase NAD+in liver within 15 minutes.
NMN seems to be absorbed into cells through molecular transporters embedded in the cell surface. NMN molecules are smaller than NAD+and can be more effectively absorbed into cells. Because the cell membrane presents a barrier, NAD+cannot easily enter the human body. The membrane has water-free space, which can prevent ions, polar molecules and macromolecules from entering without using transport proteins. It was thought that NMN must be changed before entering the cell, but new evidence shows that it can enter the cell membrane directly through NMN-specific transport protein.
In addition, the injection of NMN will lead to the increase of NAD+in many areas of the body (including pancreas, adipose tissue, heart, skeletal muscle, kidney, testis, eyes and blood vessels). Oral administration of NMN in mice will increase NAD+in liver within 15 minutes.
NMN fast conversion to NAD+
Safety and side effects of NMN
NMN is considered safe in animals, and its results are encouraging. Human trials have begun. Even in mice and human studies, even at high concentrations, the molecule is considered safe and non-toxic. Long-term (one year) oral administration of mice has no toxic effect. The first clinical trial in humans has been completed, and the evidence supports the idea of single dose non-toxic.
Although a study for men published in November 2019 showed that the bilirubin level in the blood of subjects after taking NMN increased, these levels remained within the normal range. Future research should focus on long-term safety and efficacy. NMN is not associated with any other known side effects.
NMN is considered safe in animals, and its results are encouraging. Human trials have begun. Even in mice and human studies, even at high concentrations, the molecule is considered safe and non-toxic. Long-term (one year) oral administration of mice has no toxic effect. The first clinical trial in humans has been completed, and the evidence supports the idea of single dose non-toxic.
Although a study for men published in November 2019 showed that the bilirubin level in the blood of subjects after taking NMN increased, these levels remained within the normal range. Future research should focus on long-term safety and efficacy. NMN is not associated with any other known side effects.
The future of NMN
NMN has shown encouraging therapeutic properties in animal studies, and researchers aim to understand the role of this molecule in human body. A recent clinical trial in Japan showed that the molecule was safe and well tolerated under the dosage. More research and human trials are under way. This is a fascinating multifunctional molecule, and we still need to learn a lot.
NMN has shown encouraging therapeutic properties in animal studies, and researchers aim to understand the role of this molecule in human body. A recent clinical trial in Japan showed that the molecule was safe and well tolerated under the dosage. More research and human trials are under way. This is a fascinating multifunctional molecule, and we still need to learn a lot.


